World Hydrogen Week

How will regulation, standardisation, and certification work together?
This question we discussed 09.10.2025 during the World Hydrogen Week in Copenhagen, organised by World Hydrogen Leaders.
Under the chair of Kim Talus and the moderation of Ulrike Hinz, together with Régis Prévost and Mohit Agrawal, we explored how standards and regulation interact in the production of hydrogen and hydrogen derivatives.


This topic is also part of my ongoing research at the University of Eastern Finland. Building on my previous studies, I shared several key points during the discussion:
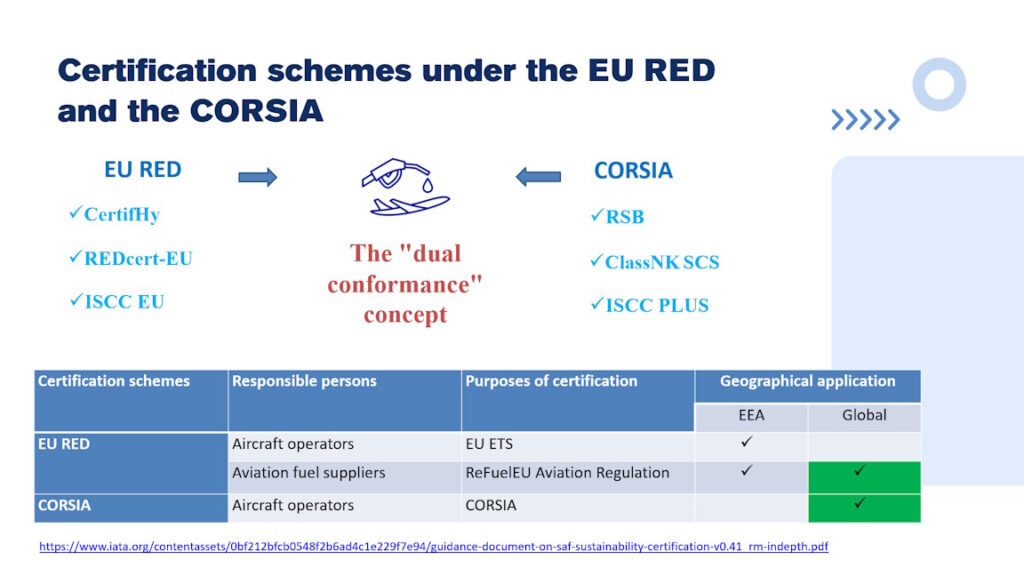
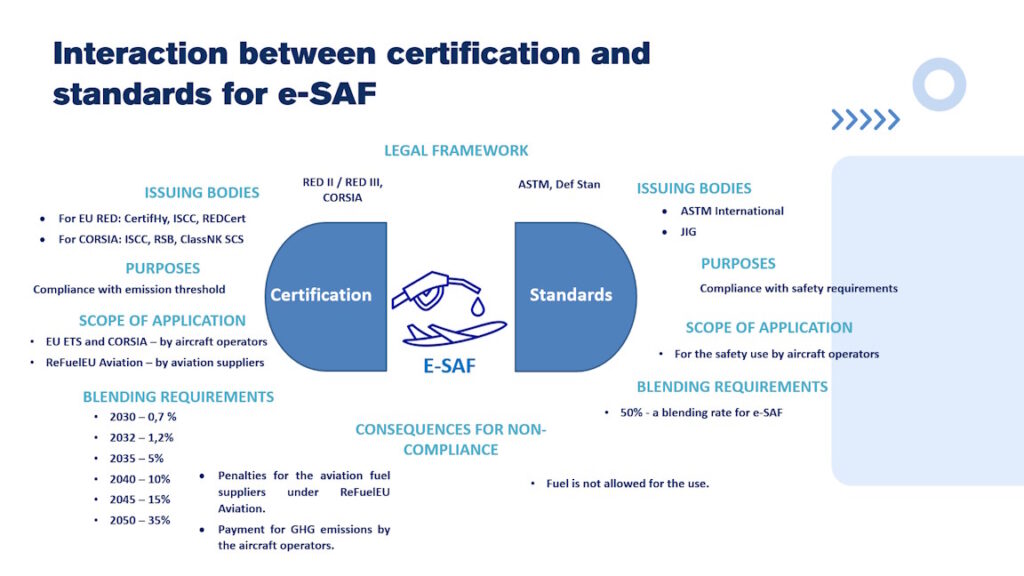
📌 Different purposes: Regulations aim primarily at achieving greenhouse gas (GHG) emission reduction targets, while standards focus on ensuring safety and technical compatibility.
📌 Different approaches to blending: Regulations allow flexibility through book & claim or mass balance systems, whereas standards typically apply only to physical blending.
📌 Different consequences for non-compliance: Under regulatory frameworks, penalties or GHG payments may apply, while under technical standards, non-compliance simply means the fuel cannot be used.
It was a truly insightful exchange on how these frameworks can and must align to support the development of a global hydrogen economy.